*Disclaimer: All content and information in this blog is for informational and educational purposes only.

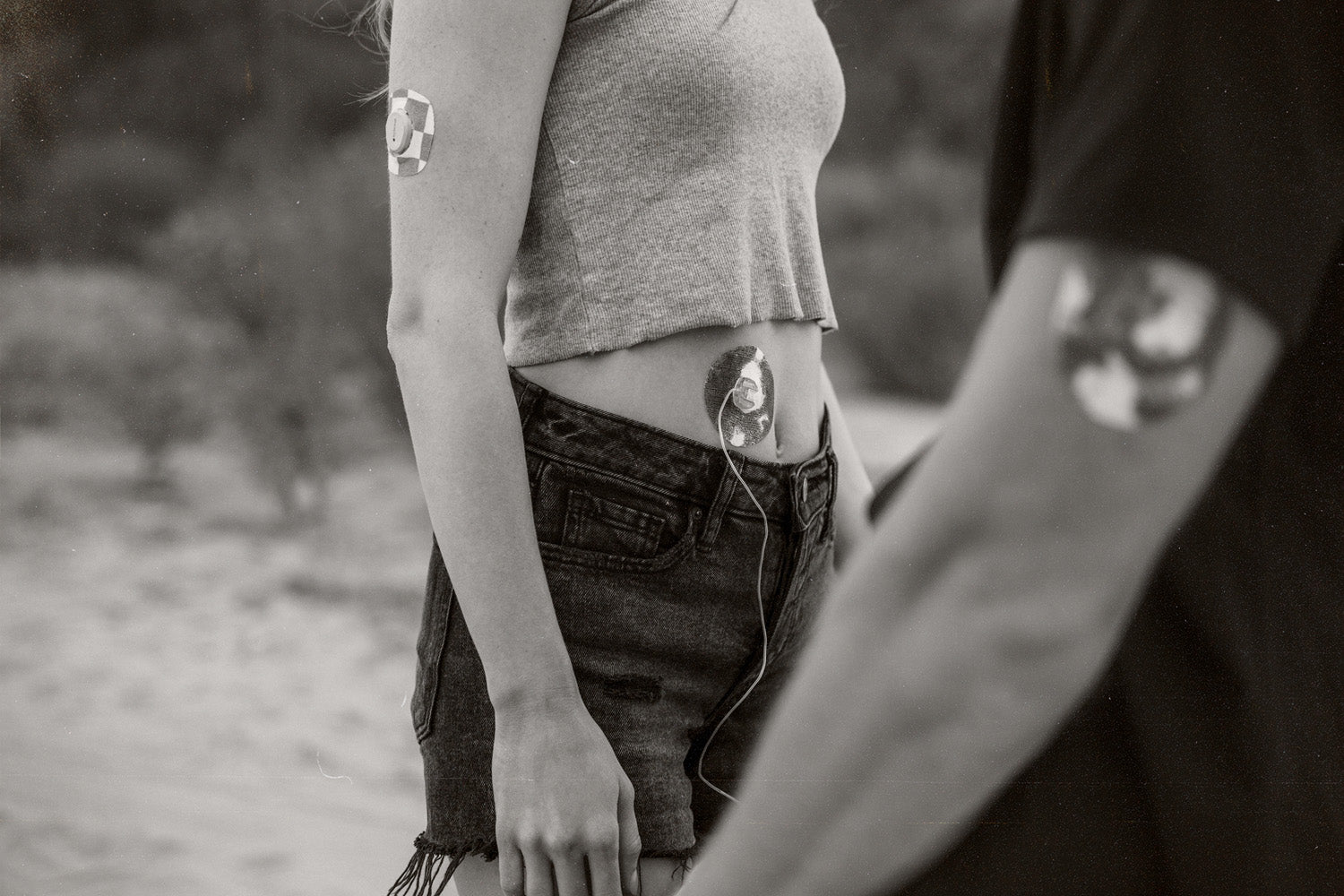
Healthcare providers often advise people with diabetes to engage in regular exercise due to its numerous health benefits. However, exercising with diabetes requires some caution. While it is commonly known that hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can occur during physical activity, there are instances where blood sugar levels may actually rise during or after exercise. This raises the question: why does your blood sugar rise, instead of fall, and how can you effectively manage it? Keep reading to find out!

Why might blood sugars increase with exercise?
The rise in blood sugar during exercise is a result of your body functioning the way it was intended. Various intricate mechanisms come into play, so let’s break them down:
Intensity of the workout:
The level of intensity at which your body is working during exercise can affect your blood sugar levels. Higher intensity workouts, where your body is working harder and the energy demand is greater, can lead to higher blood sugar levels. This is because your body may need to rely on sources other than oxygen to meet the energy demand, such as liver glucose release, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Some examples of physical activity that may increase blood sugar include: high-intensity interval training (HIIT), heavy strength training, sprints, and competitive sports.
Carbohydrate intake:
The intake of carbohydrates before or during a workout can play a significant role in increasing your blood sugar levels. Individuals with diabetes are generally advised to always have a snack before exercising. If you consistently find that your blood sugar levels are elevated after a workout and you’ve been snacking before exercise, it is possible that you are consuming too many carbohydrates beforehand. The amount of carbohydrates you consume should be based on factors such as the intensity and duration of your workout as well as your pre-exercise blood sugar level. Below is a chart adapted from Diabetes Motion that provides general recommendations for carbohydrate intake during physical activity.

*Disclaimer: Please note that these are general recommendations and individual needs may vary. It's essential to work with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance on managing your blood sugar levels during exercise.
Pre-workout insulin adjustments:
Many individuals with diabetes make adjustments to their insulin dosing before physical activity in order to prevent a hypoglycemic episode, This often involves temporarily decreasing basal rates, suspending insulin delivery, or reducing insulin coverage for a meal or snack. However, if these adjustments are made too early or are reduced too significantly, it can lead to high blood sugar levels during or after working out. Finding the appropriate balance between the timing of insulin adjustments and exercise to prevent both hypo- and hyperglycemia can be challenging. Working with your healthcare team can help you with determining the appropriate insulin modifications for your specific exercise routine.
Strategies to keep blood sugars in range during exercise
Having learned about the factors that can contribute to a rise in blood sugars during or after exercise, you might be wondering how to maintain in range blood sugar levels. It can be frustrating and discouraging when your blood sugar fluctuates, especially when you are doing all you can to keep them in range. With some minor tweaks, you can achieve more predictable blood sugar levels during your workouts. For a closer look at some of these strategies, check out this blog post here.
Understanding the reasons behind high blood sugar levels after exercise can be eye-opening for people with diabetes. You can begin to work towards implementing appropriate strategies for maintaining in range blood sugars during and after your workouts so it no longer feels like a guessing game.
Check out Keeping it 100 Radio: Uncensored Diabetes Conversations Episode 92: Why Are Your Blood Sugars High After Exercise with Type 1 Diabetes? Explained. Available on Spotify and Apple Podcasts.
This article was medically reviewed by Amanda Ciprich, MS, RD. Last updated on 7/17/23.