*Disclaimer: All content and information in this blog is for informational and educational purposes only.
Living with diabetes can be quite a challenge. From monitoring your blood glucose levels to staying active and eating healthily, it can feel like there are so many things to keep track of. However, there's one crucial aspect of diabetes care that you shouldn't overlook: regular checkups with your healthcare provider. Not only can these visits help you stay informed about your condition, but they can also help you catch any potential issues early and prevent complications down the road. So, if you've been putting off that health exam, now is the time to schedule it! Whether it's bloodwork, a dental checkup, or an eye exam, taking proactive steps today can help you prepare for a healthier future. Want to learn more? Check out our latest blog post on the importance of regular checkups for people with diabetes.
Importance of routine health screenings for diabetes
People with diabetes are at an increased risk for developing health conditions such as heart disease, kidney disease, and other autoimmune conditions. Regular health screenings and tests can detect early signs of potential complications, which can lead to early treatment and better management of the condition.
How frequently should you get bloodwork with diabetes?
The frequency of blood work for people with diabetes will vary depending on your individual health status and healthcare providers recommendations. In general, people with diabetes should have their blood work taken at least once a year to monitor their blood glucose levels, heart health, kidney function and other health indicators. Healthcare providers may recommend more frequent blood work, such as every three to six months, for people who are taking new medications or have other health concerns. It’s important for you to discuss the recommended frequency of blood work with your healthcare provider.
Routine Diabetes Testing

Assessing blood glucose levels is an essential component during routine diabetes care visits. Fasting glucose, Hemoglobin A1C and time-in-range can be used to assess the effectiveness of your current diabetes management plan and determine if any adjustments are necessary.
Important Tests for Diabetes
- Fasting glucose
- Hemoglobin A1C
- Time in Range
Fasting Glucose
Fasting glucose is an important test for people with diabetes because it measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast. This test is used to diagnose and monitor diabetes, as well as to evaluate how well diabetes is being managed. While fasting glucose targets differ for each individual, the American Diabetes Association recommendations fasting glucose levels to be between 80-130 mg/dL.
Hemoglobin A1C
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a blood test that measures the average blood glucose levels over a period of 2-3 months. The American Diabetes Association recommends maintaining an HbA1c level of less than 7%, although target levels may vary based on age, duration of diabetes, and the presence of other chronic conditions. Typically, HbA1c levels should be tested at least twice a year for individuals with well-controlled diabetes, and more frequently for those with uncontrolled diabetes. If an individual consistently has HbA1c levels above target levels, they may require more frequent testing, such as every three months, to make timely adjustments to their treatment plan.
Time in Range
Time in range (TIR) refers to the amount of time a person with diabetes spends with their blood glucose levels within a target range. TIR is becoming increasingly recognized as an important metric for diabetes management, as it provides a more complete picture of a person's glucose control over time. While traditional glucose targets have focused on fasting glucose levels and HbA1c, TIR provides a more nuanced view of glucose control by tracking fluctuations throughout the day, including post-meal spikes and overnight lows. The American Diabetes Association recommends a TIR of at least 70% for people with diabetes, with a target range of 70-180 mg/dL. However, individual goals may vary based on factors such as age, duration of diabetes, and other health conditions. Regular monitoring of TIR can help individuals and their healthcare providers make adjustments to their diabetes management plan to achieve better glucose control and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Routine Heart Disease Testing
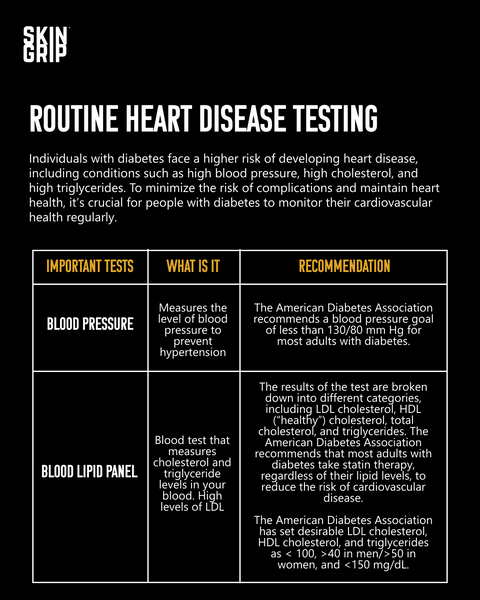
Individuals with diabetes face a higher risk of developing heart disease, including conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high triglycerides. To minimize the risk of complications and maintain heart health, it's crucial for people with diabetes to monitor their cardiovascular health regularly. This includes routine checks of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides levels to identify any potential concerns and make timely adjustments to their treatment plan. By staying up-to-date about their heart health, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of heart disease and related complications.
Heart Disease Tests for People with Diabetes
- Blood pressure
- Triglycerides
- Cholesterol
- HDL Cholesterol
- LDL Cholesterol
Blood Pressure
People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Hypertension can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage in people with diabetes. The American Diabetes Association recommends a blood pressure goal of less than 130/80 mm Hg for most adults with diabetes. It is important for people with diabetes to regularly monitor their blood pressure and work with their healthcare team to manage it through lifestyle changes, medication, or a combination of both.
Blood Lipid Panel
The lipid panel is a blood test that measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels in your blood. High levels of LDL ("lousy") cholesterol and triglycerides are common in people with diabetes and can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. The results of the test are broken down into different categories, including LDL cholesterol, HDL ("healthy") cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. The American Diabetes Association recommends that most adults with diabetes take statin therapy, regardless of their lipid levels, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is important to discuss target numbers, lifestyle interventions and potential statin therapy with a healthcare provider. The American Diabetes Association has set desirable LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides as < 100, >40 in men/>50 in women, and <150 mg/dL.
Kidney Disease

People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing kidney disease due to potential injury to the small blood vessels. Impaired kidney function can result in the accumulation of harmful waste products in the body. To prevent complications and preserve kidney function, it's important for individuals with diabetes to undergo annual evaluation of their kidney function. There are various tests available, such as albumin-to-creatinine ratio, BUN, and eGFR blood and urine tests, which can be used to assess kidney function. By closely monitoring their kidney health and identifying any issues early, individuals with diabetes can take proactive measures to maintain their overall health and kidney function.
Kidney Function Tests for People with Diabetes
- Albumin-to-creatinine ratio
- BUN
- eGFR
Albumin-to-creatinine ratio
A urine test that measures the amount of albumin in your urine can be an important tool for monitoring kidney health, particularly for people with diabetes who are at increased risk for kidney disease. Albumin is a type of protein and too much of it in the urine can be a sign of kidney damage. Early detection of kidney damage is crucial as prompt treatment, combined with well-managed blood glucose and blood pressure, can prevent or slow the progression of chronic kidney disease. The target number for albumin in the urine is less than 30 mg/g of urine creatinine. For people with type 2 diabetes or those who have had type 1 diabetes for at least five years, this test should be done once a year. However, if a previous test has shown levels above the target, more frequent testing may be necessary.
BUN
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is a test that measures the amount of nitrogen in the blood that comes from urea, which is a waste product of protein metabolism. For people with diabetes, BUN level is an important indicator of kidney function. If the kidneys are not functioning properly, the level of BUN in the blood can become elevated, indicating that the body is not able to eliminate waste effectively. Regular monitoring of BUN level is crucial for individuals with diabetes to assess kidney function and detect any potential issues early.
eGFR
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is a measure of your kidney function. It is determined through a blood test that takes into account your creatinine levels, age, and gender, and estimates your kidney's ability to filter waste. The eGFR score is used to identify the stage of kidney disease, and the treatment plan is tailored accordingly. Knowing your eGFR score can help your healthcare provider determine the best course of action to preserve your kidney function and manage any existing kidney disease.
Thyroid Disease

When someone has diabetes, it is crucial to have their thyroid function tested because these two conditions frequently coexist as they are both endocrine disorders. The thyroid gland plays a critical role in regulating the body's metabolism, which includes the processes of energy usage and storage, by producing thyroid hormone. If the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, it can result in hyperthyroidism and a quicker metabolism. Conversely, if too little thyroid hormone is produced, it can lead to hypothyroidism and a slowdown of bodily functions.Regular thyroid function testing allows healthcare professionals to detect any thyroid issues early and manage them appropriately, which can lead to improved diabetes management and overall health. By keeping a close watch on both conditions, individuals with diabetes can proactively manage their health and reduce the risk of complications.
Thyroid Tests for People with Diabetes
- T4/T3
- TSH
Celiac Disease

Type 1 diabetes and celiac disease are autoimmune disorders that share similar genetic and environmental risk factors. It has been observed that individuals with type 1 diabetes have a higher likelihood of having celiac disease than the general population. Therefore, it is recommended that people with type 1 diabetes get tested for celiac disease. Antibody testing is commonly used to detect celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder that is triggered by consuming gluten. The blood tests measure the presence of three different antibodies: IgA, IgG, and tissue transglutaminase (tTG), and require the individual to be consuming gluten in order to detect any abnormal antibody levels. If these tests show higher than normal levels of these antibodies, it may indicate that the body is producing an autoimmune response to gluten. Early detection and management of celiac disease is crucial to prevent complications and improve the quality of life for individuals with gluten intolerance or sensitivity. Proper dietary interventions can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Celiac Disease Tests for People with Diabetes
- Antibody testing: IgA, IgG, tTG
Annual Eye Exams for Diabetes

Annual eye exams are crucial for people with diabetes because they are at a higher risk of developing eye complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts. These conditions can cause vision loss and even blindness if not detected and treated early. Diabetic retinopathy, for example, is a leading cause of blindness in adults and occurs when high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels in the retina. However, early detection and treatment can prevent or slow the progression of these conditions. During an eye exam, an eye doctor can check for signs of eye damage, monitor changes over time, and recommend appropriate treatment, such as laser surgery or medication. Therefore, regular eye exams are essential for maintaining good vision and preventing serious eye problems in people with diabetes.
Foot Exams for People with Diabetes

Foot exams are a crucial part of diabetes care as people with diabetes are at risk for foot complications such as nerve damage, poor circulation, and slow healing wounds. Regular foot exams can help identify any issues early on and prevent them from becoming more serious. During a foot exam, healthcare providers will check for any signs of nerve damage, poor circulation, or foot deformities. They will also inspect for any cuts, blisters, or sores that may have been overlooked due to nerve damage. Individuals with diabetes should have their feet checked at least once a year, but may need to be seen more frequently if they have any foot problems or complications.
Dental Exams

Dental exams are important for people with diabetes because they are at a higher risk of developing oral health problems. High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and fungal infections in the mouth. Dental exams can help detect and treat these issues early on, preventing more serious problems from developing. During a dental exam, a dentist can check for signs of gum disease, such as inflammation or bleeding, and provide guidance on proper oral hygiene practices. People with diabetes should schedule regular dental check-ups, maintain good oral hygiene habits, and inform their dentist about their diabetes and any medications they are taking to ensure comprehensive care.
Regular checkups with your healthcare provider are one of the most crucial components of diabetes care. By maintaining routine visits, you can stay informed about your condition, catch any potential issues early, and prevent complications from arising. Remember, taking proactive steps today can prepare you for a healthier future.
Tune in to Keeping it 100 Radio: Uncensored Diabetes Conversations- Episode 94 to gain insight on routine testing and its importance for diabetes care. Join your host, Lissie Poyner, as she speaks with Amanda Ciprich, MS, RD, a Registered Dietitian, about the significance of these tests. The episode is now available on Spotify and Apple Podcasts for you to listen and learn.
Written By: Amanda Ciprich, MS, RD
Founder of T1D Nutritionist
Website: www.t1dnutritionist.
Instagram: @t1d.nutritionist