(k-e-k-u-l-e / pixabay)
(k-e-k-u-l-e / pixabay)
If you have someone in your life who has been diagnosed with diabetes, there is a chance you don’t know which type they have. Many people who do know what type they have don’t fully understand the difference between the two types of diabetes mellitus. We want to clear up your questions and confusion.
What is diabetes? Why are there two types?
When we are talking about diabetes, we usually mean diabetes mellitus, as opposed to another condition called diabetes insipidus. Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the amount of glucose in your bloodstream is unusually high. The word “mellitus” means “sweet” and is related to the Latin word for honey, “mel.” In the days before medical testing, diabetes was detected by tasting urine. As the high blood sugar made the urine sweet, the condition was named after that honey-like sweetness.
There are two types of diabetes mellitus, which we differentiate based on the underlying cause of high blood sugar. Both types also involve the hormone insulin, which is produced by certain cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows the body’s cells to absorb glucose out of the bloodstream.
When the body is unable to use insulin to regulate blood sugar, significant problems arise. High blood sugars can cause nerve damage, damage to the body’s organs, blindness, and leave the body vulnerable to infections. In many cases, uncontrolled blood sugars can cause death. Because of this, it is of the utmost importance to appropriately manage diabetes, regardless of type. While people with diabetes can live long, productive lives, they must pay attention to their condition daily.
Type 1
Type 1 diabetes is generally a genetic condition that develops in childhood or early adulthood. As a result, it is often called juvenile diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the cells of the pancreas that produce insulin are destroyed or injured. Because the pancreas fails to function properly, the body lacks insulin to absorb blood sugar. This causes the blood sugar to rise uncontrollably, without a way to fix it. People with type 1 diabetes must use insulin injections to control their blood sugar. Without it, their blood sugar will continue to rise until they die.
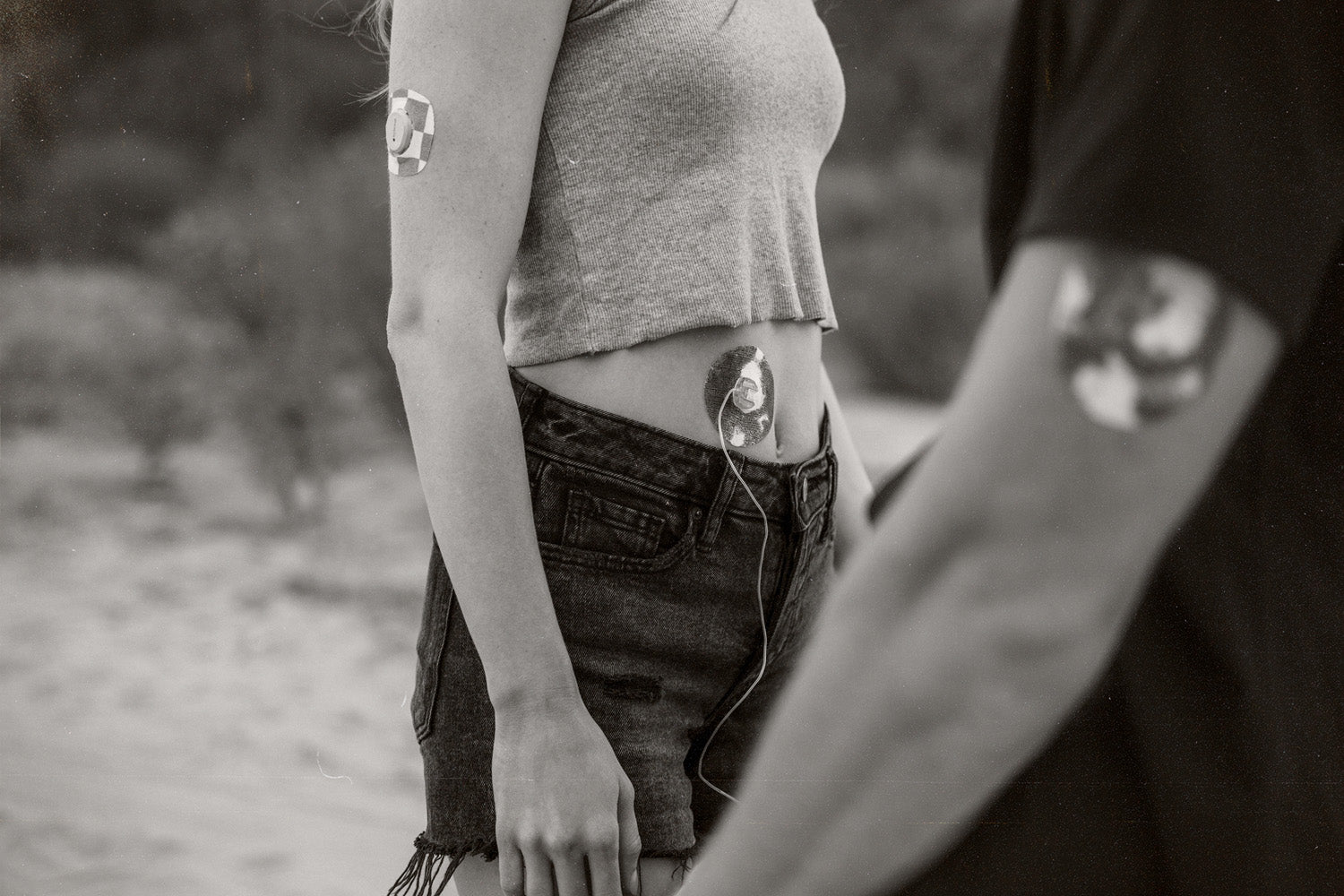
Because people with type 1 diabetes must pay close attention to their blood sugar, they frequently use CGMs or Continuous Glucose Monitors to measure their blood sugar in real-time. These sensors, such as the Freestyle Libre, Dexcom G6, or Guardian sensor, are connected to the user with tape or adhesive patches. They measure the user’s blood sugar at regular intervals and display it either on the device or on a smartphone. CGMs connected to insulin pumps will regulate the insulin released by the pump.
Type 2
Type 2 diabetes is more often developed in adulthood. Unlike in type 1 diabetes, a person with type 2 diabetes can still produce insulin in their pancreas. Though they produce insulin, the body’s cells become less sensitive to the presence of insulin, which prevents the cells from absorbing glucose effectively. Because the cells do not absorb glucose from the bloodstream, the individual’s blood sugar rises.
People with type 2 diabetes are frequently able to control their blood sugar with oral medication, though many people with type 2 diabetes may eventually become insulin-dependent as their condition progresses. In these cases, people with type 2 diabetes also rely on insulin to regulate their blood sugar and may become extremely sick without regular injections. While type 1 diabetes is primarily a genetic condition, type 2 diabetes is caused by an array of factors, including genetics, the environment, and lifestyle.
What do both types have in common?
Both types of diabetes are entirely manageable conditions. At Skin Grip, we believe that people with diabetes can live fearlessly by taking their diabetes management into their own hands. The first step is to understand the condition, then work with a physician to manage it daily.
Both types of diabetics must monitor their blood sugar daily, control their diet, and exercise frequently. Additionally, both types of diabetics may suffer from similar complications, such as neuropathy, loss of sensation in periphery extremities, eye problems, skin infections, and hypo/hyperglycemia. Because the potential complications of both types of diabetes are severe, people with either type must be vigilant to maintain their long-term health.
While people with diabetes are united in our struggles, we are also united by the bad-assery it takes to overcome the hassle and live an extraordinary life. Regardless of how our bodies work, we are still athletes, students, parents, warriors, and so much more.
Diabetes is only a small aspect of who you are, which is why Skin Grip works tirelessly to make products that accommodate your unique lifestyle. Use our ultra-strong, waterproof tape to hold your diabetic sensor in place. Then move forward and put your full personality on display.
Infographic
Many people are diagnosed with diabetes. You probably know someone, but do you know what type of diabetes they have? Do you even know what diabetes is and that it has two kinds? If you want to support your loved ones with diabetes, the first step is to know the difference between the two. Read this infographic.