*Disclaimer: All content and information in this blog is for informational and educational purposes only. Last updated March 7, 2024.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring systems (CGMs) are medical devices that measure blood glucose concentrations at regular intervals for people with diabetes. While a traditional blood sugar meter provides a “snapshot” of glucose levels at a single moment in time, CGMs can provide valuable insights about blood glucose levels day and night. This allows people with diabetes to make more informed decisions by understanding how physical activity, diet, medications, and other factors affect blood sugar levels. This blog post will talk about how CGMS work and their benefits.
How CGMs Work
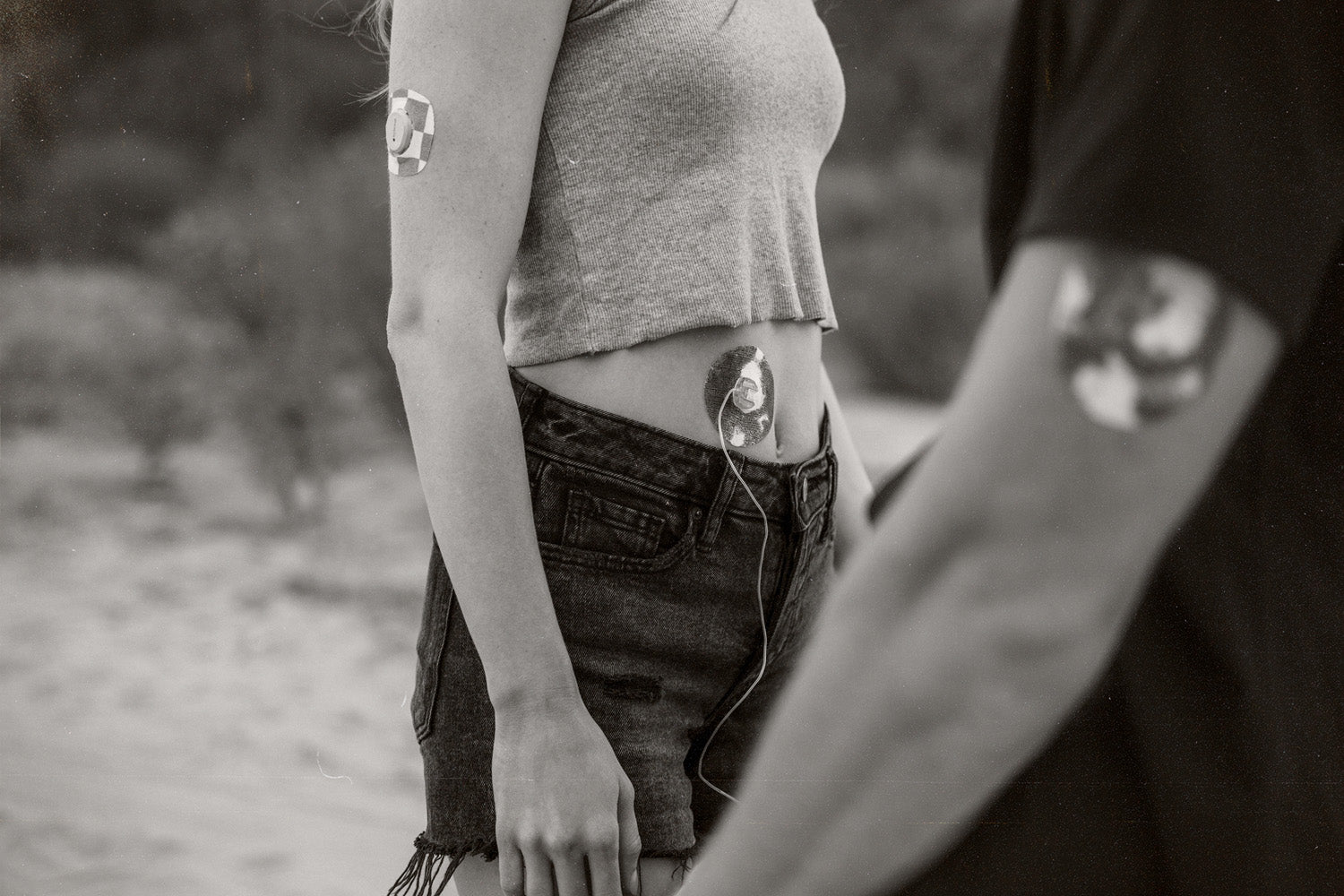
There are a few CGMs currently available on the market, but the majority of the systems include 3 main parts: sensor, transmitter and receiver.
Sensor
CGM sensors include a thin cannula that is easily inserted directly under the skin, usually on the abdomen or arm. This will measure the glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid that is a similar reading to blood glucose. The sensors are held in place with a small adhesive and require replacing every 7-14 days depending on the manufacturer.
Transmitter
CGM sensors will connect to a transmitter that wirelessly transmits blood glucose readings to a monitor or integrated insulin pump.
Receiver
The receiver is responsible for displaying blood glucose readings in addition to seeing how blood glucose readings have been trending over time. The receiver can also alert users when their blood glucose levels are too high or too low. CGM receivers can be a separate device or part of an insulin pump. Some CGM manufacturers have smartphone applications that allow blood glucose readings to be displayed on compatible devices.
Benefits of CGMs for People with Diabetes
CGMs Make Identifying Blood Glucose Patterns Easier
One of the biggest obstacles for people with diabetes is being able to understand their blood glucose patterns. CGMs make identifying blood glucose patterns easier since users can see how their daily activities affect their blood glucose levels in-real time. CGMs make it easier for individuals to identify how diet, exercise, sleep, and stress influence their blood glucose readings. This information can be helpful in making adjustments to their self-management to better control blood glucose levels.
CGMs Provide Helpful Alarms and Arrows
CGMs provide users with alarms and arrows that can influence diabetes decision making by taking action before blood glucose levels become too high or too low. These alerts can be customized based on individual glucose target levels which can be helpful especially during periods of activities or people with diabetes who are pregnant. An example of alarms that CGMs can provide are:
- High and Low Glucose Alerts: alerts users when blood glucose levels are above or below their target range so users can take action as needed.
- Urgent Low Alerts: Urgent or severe low blood sugar levels can lead to seizures or loss of consciousness if left untreated. Urgent low alerts are designed to send an attention-grabbing alarm to users so they can take immediate action to raise blood glucose levels as soon as possible.
- Rapid Rise/Fall Alerts: Rapid rise and fall alerts indicate how quickly blood glucose levels are changing. This information can help users make more informed decisions, especially if their blood sugar is trending too high or too low very quickly.
- Low Soon: Predictive alerts, like low soon alarms, can notify users of a potential low blood sugar before it occurs. These alerts can allow individuals to take action before blood sugar levels are dangerously low.
No fingersticks
Unlike a regular blood sugar meter that requires multiple finger pricks daily, CGMs only need to be placed into the skin one time and can last up to 14 days. Most CGMs do not require finger sticks since they come factory calibrated and do not require users to calibrate with finger sticks. This makes the CGM a great option for people who find traditional blood sugar checks painful or find that finger sticks interfere with their daily activities.
Informed Decisions for Users and Their Families
CGMs easily provide important blood sugar information directly to users and their families. CGM data is transmitted wirelessly to compatible devices that users and families can view throughout the day and night and as needed. With a CGM, there is no more guessing about what blood sugar levels are doing again. Users will know right away if their blood sugar is running high or low and can make adjustments accordingly. No more “I think I might be low, but I’m not sure” moments and no more “I'm sure my blood sugar is fine because I really don’t want to poke myself” excuses. This makes blood sugar readings incredibly accessible so that users and families are always informed about current and future blood sugar readings during critical times like sleep, activity, sleepovers, and more.
Lower A1C and Improve Time in Range
Research has shown that CGMs can lower A1C and improve time in range for individuals with diabetes. Since blood sugar readings are displayed in-real time, people with diabetes can make adjustments to their daily activities and medications in a timely manner. For example, if someone notices that their blood sugar levels tend to drop too low after eating certain foods, they can make adjustments to their diet or medication in order to prevent those drops from happening. Additionally, these insights provide valuable information for healthcare providers so they can provide a more personalized plan for caring for your diabetes.
To learn more about CGMs and how they can help your diabetes, check out these resources:
Diabetes Devices Up Close: Dexcom G6 Edition
Diabetes Devices Up Close: The Eversense 3
Diabetes Devices Up Close: Medtronic Guardian